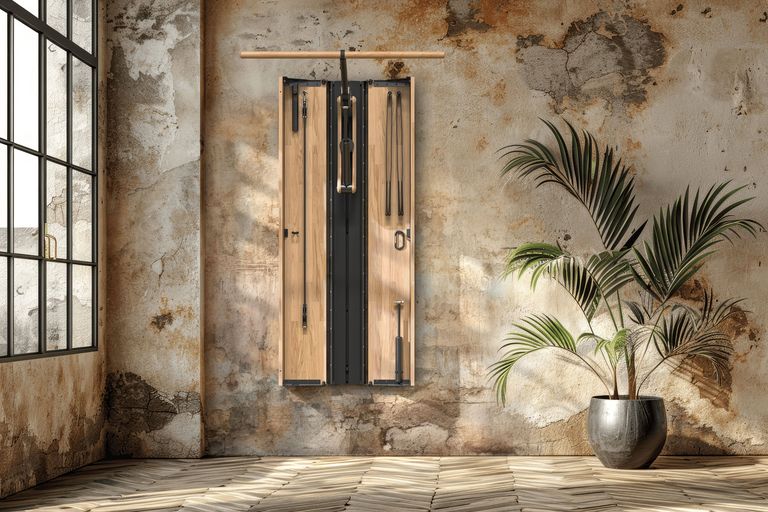
What makes this exercise particularly effective?
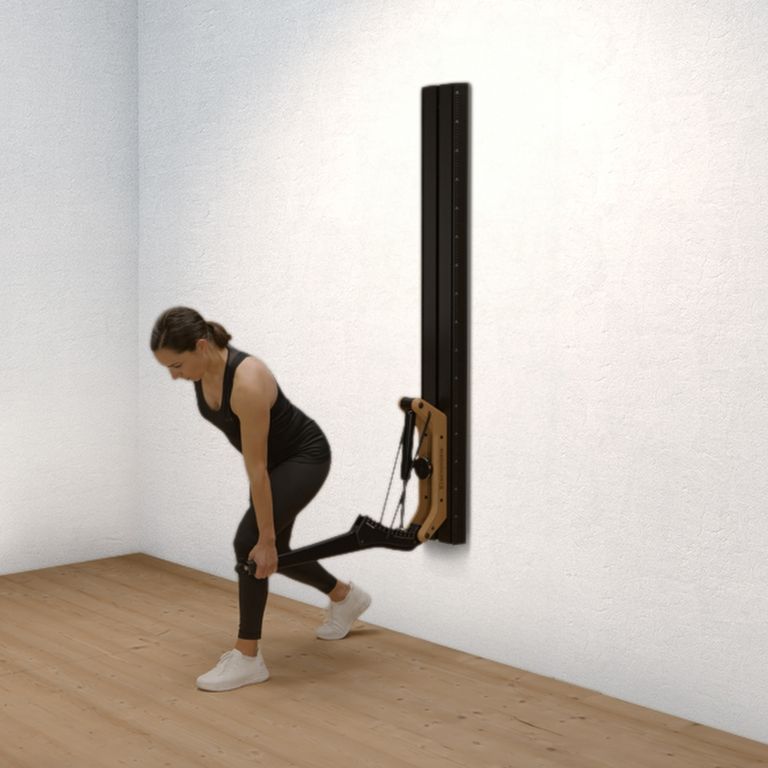
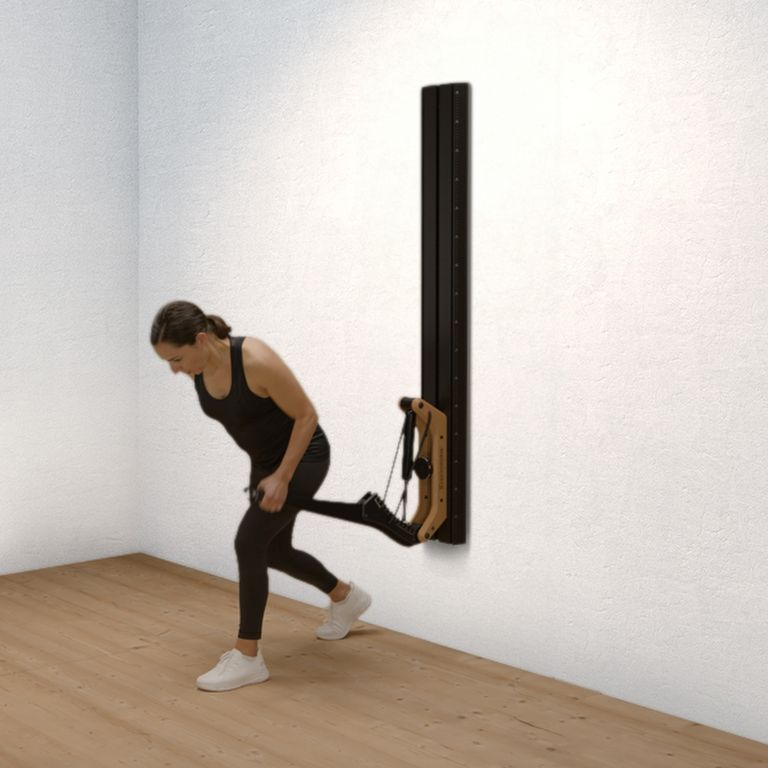
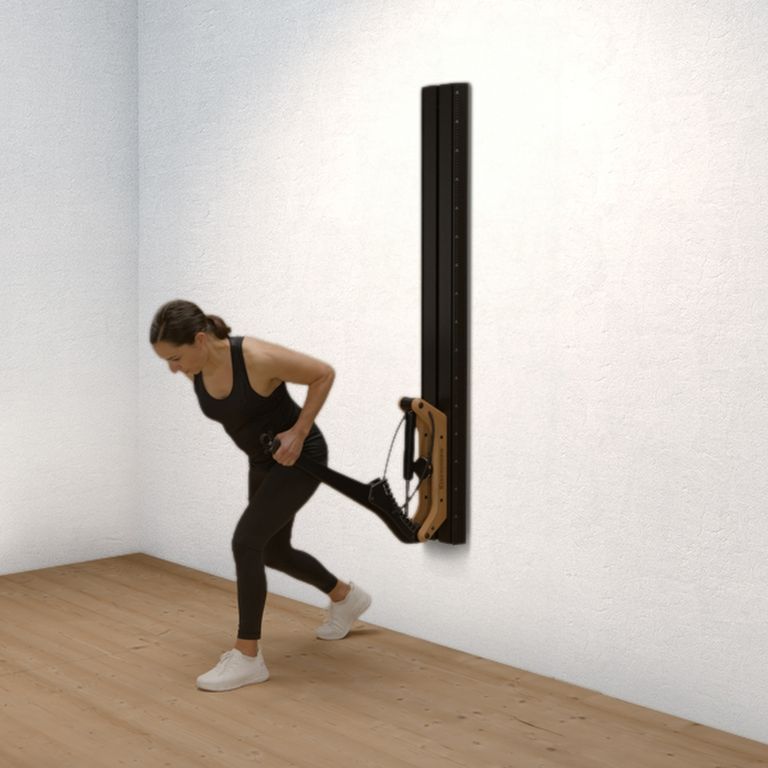
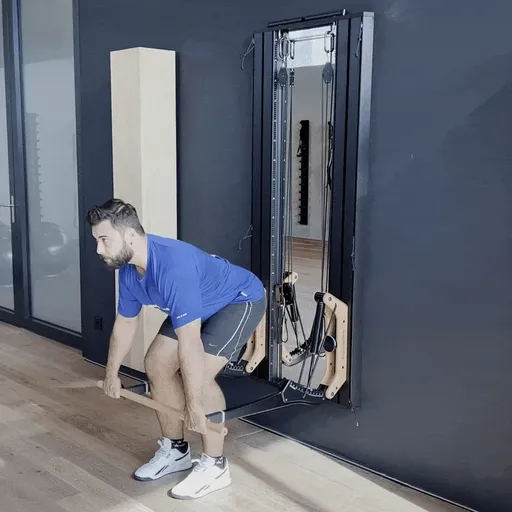
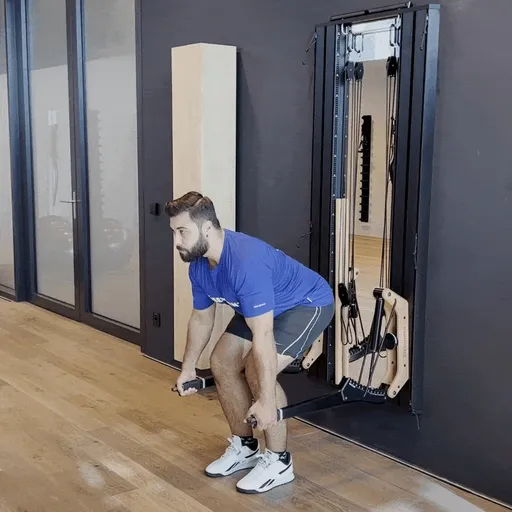
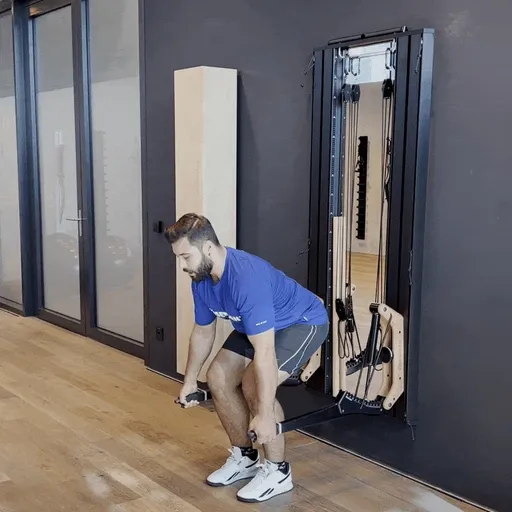
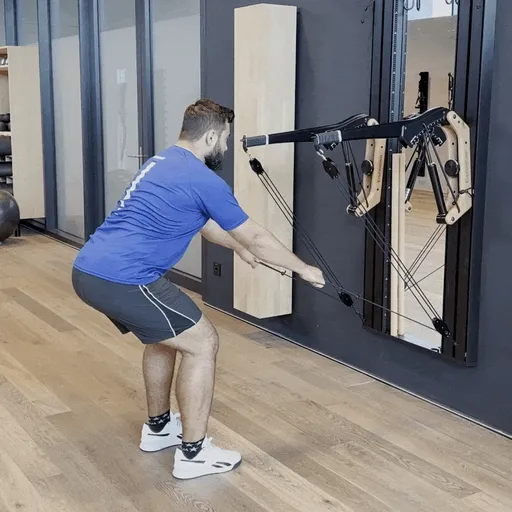
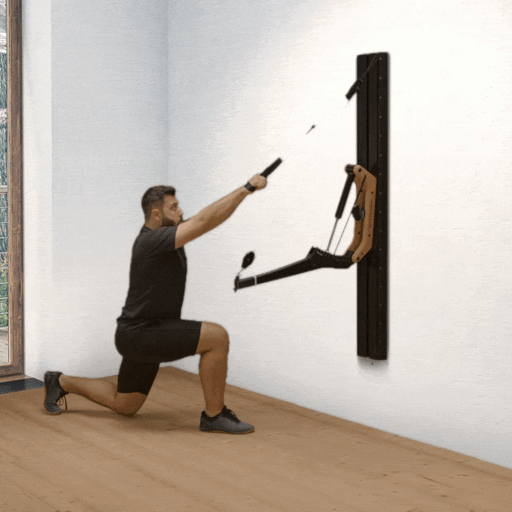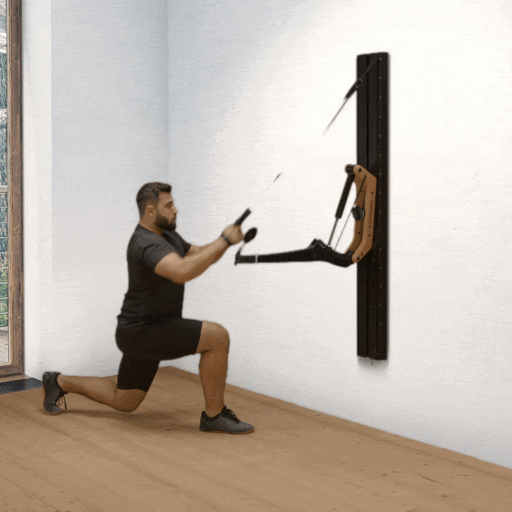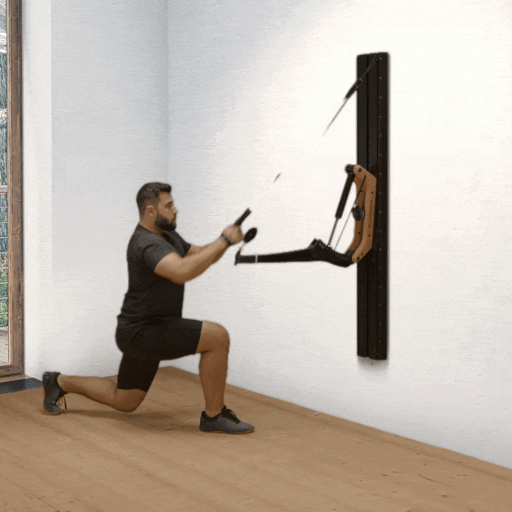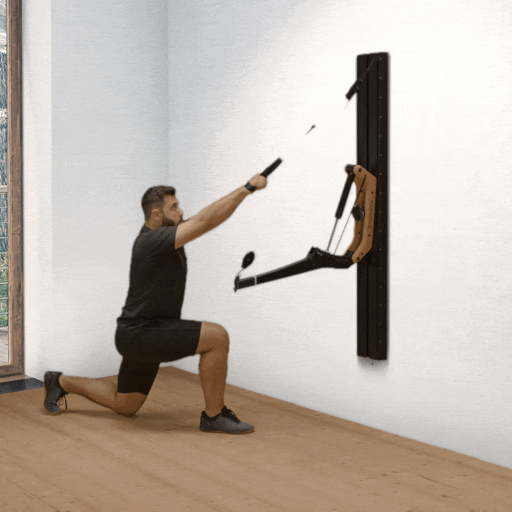
One-arm rowing is a unilateral compound exercise that trains each side of the body independently. This unilateral approach not only targets the middle and lower back—effectively activating the latissimus dorsi and rhomboids—but also enhances core stability, as rotational forces must be actively countered. This is a crucial factor for developing functional strength.
What effect does the exercise achieve?
Targeted back strengthening: Primarily works the latissimus dorsi, but also engages the posterior deltoid, rhomboids, biceps, and forearm muscles.
Improved core stability: The unilateral execution provides a strong anti-rotation stimulus, actively engaging deep core muscles such as the obliques and transverse abdominis.
Correction of muscular imbalances: Each side is trained individually, allowing weaknesses to be identified and strengthened in a targeted manner.
How does this exercise fit into the Big 5 concept?
The Big 5 include the fundamental exercises: squat, deadlift, bench press, pull-up or lat pulldown, and shoulder press. One-arm rowing can serve as an alternative or complementary exercise to the classic pull-up:
Strengthens upper body pulling movements: Supports development for exercises such as pull-ups and bench presses.
Promotes core control: The anti-rotation demand is essential for maintaining stability during complex compound movements.
Functional full-body strength: Combines pulling and stability elements, improving coordination and overall functional strength.

















)





)
